Lead-free/RoHS in Electronic Components
- Home
- /
- POSTS
- /
- Technology
- /
- Lead-free/RoHS in Electronic Components
RoHS stands for Restriction of Hazardous Substances.
Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS) of the use certain hazardous substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union.
All products in the EU market after July 1, 2006 must pass RoHS compliance.Today, Lead-free is equivalent to RoHS compliant, because Pb-free components are very rarely not compliant with RoHS directive. Some products are called “RoHS 5/6” because RoHS compliant excepted the finish which is SnPb used in Space and some Military markets to avoid pure Tin.
The most popular alternative to the SnPb solder paste is the SnAgCu solder paste, with a melting point 35°C higher than the previous one.
For electronic components, targets are :
• Proposition of devices without Pb in package terminals (leads, balls, bumps) compatible with the new solder.
• Compatibility of packages (molding compound, die attach material, ceramics) with Pb-free process .
• Compatibility with both SnPb and Pb-free solder pastes during the transition phase.
TIN WHISKERS
What are Tin Whiskers?
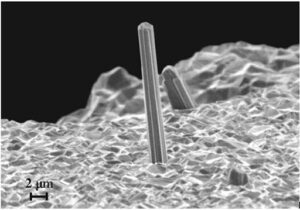 Tin whiskers are electrically conductive, crystalline structures of tin that sometimes grow from surfaces where tin (especially electroplated tin) is used as a final finish.
Tin whiskers are electrically conductive, crystalline structures of tin that sometimes grow from surfaces where tin (especially electroplated tin) is used as a final finish.
Tin whiskers have been observed to grow to lengths of several millimeters (mm) and in rare instances to lengths in excess of 10 mm.
Numerous electronic system failures have been attributed to short circuits caused by tin whiskers that bridge closely-spaced circuit elements maintained at different electrical potentials.
 Many manufacturers define pure Tin (Sn) finish as a Lead-free replacement for Tin-Lead (SnPb) on component leads for ICs, passives and connectors. Sn-whisker growth is a concern with Sn-plated components.
Many manufacturers define pure Tin (Sn) finish as a Lead-free replacement for Tin-Lead (SnPb) on component leads for ICs, passives and connectors. Sn-whisker growth is a concern with Sn-plated components.
Today, manufacturers consider to have a good mastering of Tin whisker growing on lead finishing.
First, process modification or specifications have been developed to reduce this risk. Secondly, specific tests are performed to measure the risk.
Tin whisker mitigation
Because it is not possible to completely avoid pure Tin finishes on modern boards, and because we have long life applications, we recommend to take into account the Tin whisker risk mitigation techniques proposed by JEDEC and GEIA standard documents.
Actions have to be taken into consideration:
- Qualify safe sources (applying best Manufacturing practices for Tin plating manufacturing and control)
- Monitor the presence of Tin in devices through the data base ( including the under layer when existing)
- Consider board varnishing does not eliminate the potential for whisker, but it is a mitigating measure providing a substantial protection against short circuit, excepted may be for some connectors.
RELIABILITY ISSUES
Numerous Manufacturers and Equipment makers have performed Reliability tests, first to select an alternative solution to SnPb solder alloy, secondly to confirm that the on-board reliability is sufficient to cover consumer or Industrial application domains.Other tests have been done to control the compatibility of Pb-free packages with SnPb solder process, because a mix of materials are present during the transition period.Compatibility of Pb-free components with SnPb solder is considered effective for leaded packages, even if the SnPb behavior is better with SnPb plating after comparison of the following parameters:
- Processability (visual inspection of solder joints)
- Solderability (measured through wetting force)
- On-board reliability in Temperature Cycling
New designs
Component market offer is quite exclusively on Lead-free parts today.
Using only Lead-free components on new designs minimizes short term obsolescence of leaded parts (SnPb), gives access to advanced functions only available for some of them in Lead-free version, and is compliant with the future Lead-free manufacturing process.
In the same time, as long as manufacturing processes have not switched on Lead-free processes, boards on production stage should only used components that are compatible with such processes that means SnPb components or Lead-free components that are compatible with the SnPb process (Backward compatibility).
REFERENCE :
- 2002/95/EC EU directive on Restriction on the use of Hazardous Substances (RoHS).
- NASA NEPP – Basic Information Regarding Tin Whiskers
- JEDEC JESD97 Marking, Symbols and Labels for identification of Pb-free assemblies & components.
- JEDEC J-STD-020 Moisture/reflow sensitivity classification for non-hermetic surface mount devices.
- JEDEC JESD22-A113 Preconditioning of non-hermetic surface mount devices prior to reliability testing
- JEDEC JESD201 Environmental acceptance requirements for Tin Whisker susceptibility of Tin and Tin alloy
- JESD22A121.01 Test Method for Measuring Whisker Growth on Tin and Tin alloy surface finishes.
- JP002 Current Tin whiskers theory and mitigation practices guideline.








